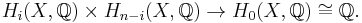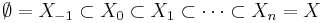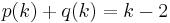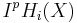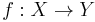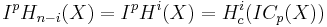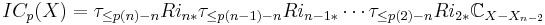Intersection homology
In topology, a branch of mathematics, intersection homology is an analogue of singular homology especially well-suited for the study of singular spaces, discovered by Mark Goresky and Robert MacPherson in the fall of 1974 and developed by them over the next few years.
Intersection cohomology was used to prove the Kazhdan–Lusztig conjectures and the Riemann–Hilbert correspondence. It is closely related to L2 cohomology.
Contents[hide] |
Goresky–MacPherson approach
The homology groups of a compact, oriented, n-dimensional manifold X have a fundamental property called Poincaré duality: there is a perfect pairing
Classically—going back, for instance, to Henri Poincaré—this duality was understood in terms of intersection theory. An element of
- Hj(X)
is represented by a j-dimensional cycle. If an i-dimensional and an (n − i)-dimensional cycle are in general position, then their intersection is a finite collection of points. Using the orientation of X one may assign to each of these points a sign; in other words intersection yields a 0-dimensional cycle. One may prove that the homology class of this cycle depends only on the homology classes of the original i- and (n − i)-dimensional cycles; one may furthermore prove that this pairing is perfect.
When X has singularities—that is, when the space has places that do not look like Rn—these ideas break down. For example, it is no longer possible to make sense of the notion of "general position" for cycles. Goresky and MacPherson introduced a class of "allowable" cycles for which general position does make sense. They introduced an equivalence relation for allowable cycles (where only "allowable boundaries" are equivalent to zero), and called the group
- IHi(X)
of i-dimensional allowable cycles modulo this equivalence relation "intersection homology". They furthermore showed that the intersection of an i- and an (n − i)-dimensional allowable cycle gives an (ordinary) zero-cycle whose homology class is well-defined.
Stratifications
Intersection homology was originally defined on suitable spaces with a stratification, though the groups often turn out to be independent of the choice of stratification. There are many different definitions of stratified spaces. A convenient one for intersection homology is an n -dimensional topological pseudomanifold. This is a (paracompact, Hausdorff) space X that has a filtration
of X by closed subspaces such that
- for each i and for each point x of Xi − Xi−1, there exists a neighborhood
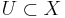 of x in X, a compact (n − i − 1)-dimensional stratified space L, and a filtration-preserving homeomorphism
of x in X, a compact (n − i − 1)-dimensional stratified space L, and a filtration-preserving homeomorphism 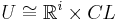 . Here
. Here 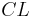 is the open cone on L.
is the open cone on L. - Xn−1 = Xn−2
- X − Xn−1 is dense in X.
If X is a topological pseudomanifold, the i-dimensional stratum of X is the space Xi − Xi−1.
Examples:
- If X is an n-dimensional simplicial complex such that every simplex is contained in an n-simplex and n−1 simplex is contained in exactly two n-simplexes, then the underlying space of X is a topological pseudomanifold.
- If X is any complex quasi-projective variety (possibly with singularities) then its underlying space is a topological pseudomanifold, with all strata of even dimension.
Perversities
Intersection homology groups IpHi(X) depend on a choice of perversity p, which measures how far cycles are allowed to deviate from transversality. (The origin of the name "perversity" was explained by Goresky (2010).) A perversity p is a function from integers ≥2 to integers such that
- p(2) = 0
- p(k + 1) − p(k) is 0 or 1
The second condition is used to show invariance of intersection homology groups under change of stratification.
The complementary perversity q of p is the one with
Intersection homology groups of complementary dimension and complementary perversity are dually paired.
Examples:
- The minimal perversity has p(k) = 0. Its complement is the maximal perversity with q(k) = k − 2.
- The (lower) middle perversity m is defined by m(k) = integer part of (k − 2)/2. Its complement is the upper middle perversity, with values the integer part of (k − 1)/2. If the perversity is not specified, then one usually means the lower middle perversity. If a space can be stratified with all strata of even dimension (for example, any complex variety) then the intersection homology groups are independent of the values of the perversity on odd integers, so the upper and lower middle perversities are equivalent.
Singular intersection homology
Fix a topological pseudomanifold X of dimension n with some stratification, and a perversity p.
A map σ from the standard i-simplex Δi to X (a singular simplex) is called allowable if
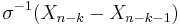 is contained in the i − k + p(k) skeleton of Δi
is contained in the i − k + p(k) skeleton of Δi
The complex Ip(X) is a subcomplex of the complex of singular chains on X that consists of all singular chains such that both the chain and its boundary are linear combinations of allowable singular simplexes. The singular intersection homology groups (with perversity p)
are the homology groups of this complex.
If X has a triangulation compatible with the stratification, then simplicial intersection homology groups can be defined in a similar way, and are naturally isomorphic to the singular intersection homology groups.
The intersection homology groups are independent of the choice of stratification of X.
If X is a topological manifold, then the intersection homology groups (for any perversity) are the same as the usual homology groups.
Small resolutions
of a complex variety Y is called a small resolution if for every r>0, the space of points of Y where the fiber has dimension r is of codimension greater than 2r. Roughly speaking, this means that most fibers are small. In this case the morphism induces an isomorphism from the (intersection) homology of X to the intersection homology of Y (with the middle perversity).
There is a variety with two different small resolutions that have different ring structures on their cohomology, showing that there is in general no natural ring structure on intersection (co)homology.
Sheaf theory
Deligne's formula for intersection cohomology states that
where ICp(X) is a certain complex of sheaves on X (considered as an element of the derived category, so the cohomology on the right means the hypercohomology of the complex). The complex ICp(X) is given by starting with the constant sheaf on the open set X−Xn−2 and repeatedly extending it to larger open sets X−Xn−k and then truncating it in the derived category; more precisely it is given by Deligne's formula
where τ≤p is a truncation functor in the derived category, and ik is the inclusion of X−Xn−k into X−Xn−k−1 and CX−Xn−2 is the constant sheaf on X−Xn−2. (Warning: there is more than one convention for the way that the perversity enters Deligne's construction: the numbers p(k)−n are sometimes written as p(k).)
By replacing the constant sheaf on X−Xn−2 with a local system, one can use Deligne's formula to define intersection cohomology with coefficients in a local system.
Properties of the complex IC(X)
The complex ICp(X) has the following properties
- On the complement of some closed set of codimension 2, we have
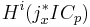 is 0 for i+m≠ 0, and for i=−m the groups form the constant local system C
is 0 for i+m≠ 0, and for i=−m the groups form the constant local system C
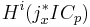 is 0 for i + m < 0
is 0 for i + m < 0- If i > 0 then
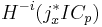 is zero except on a set of codimension at least a for the smallest a with p(a) ≥ m − i
is zero except on a set of codimension at least a for the smallest a with p(a) ≥ m − i - If i>0 then
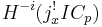 is zero except on a set of codimension at least a for the smallest a with q(a) ≥ (i)
is zero except on a set of codimension at least a for the smallest a with q(a) ≥ (i)
As usual, q is the complementary perversity to p. Moreover the complex is uniquely characterized by these conditions, up to isomorphism in the derived category. The conditions do not depend on the choice of stratification, so this shows that intersection cohomology does not depend on the choice of stratification either.
Verdier duality takes ICp to ICq shifted by n = dim(X) in the derived category.
See also
References
- Armand Borel, Intersection Cohomology (Progress in Mathematics (Birkhauser Boston)) ISBN 0817632743
- Mark Goresky and Robert MacPherson, La dualité de Poincaré pour les espaces singuliers. C.R. Acad. Sci. t. 284 (1977), pp. 1549–1551 Serie A .
- Goresky, Mark (2010), What is the etymology of the term "perverse sheaf"?, http://mathoverflow.net/questions/44149
- Goresky, Mark; MacPherson, Robert, Intersection homology theory, Topology 19 (1980), no. 2, 135–162. doi:10.1016/0040-9383(80)90003-8 MR[1]
- Goresky, Mark; MacPherson, Robert, Intersection homology. II, Inventiones Mathematicae 72 (1983), no. 1, 77–129. 10.1007/BF01389130 MR0696691 This gives a sheaf-theoretic approach to intersection cohomology.
- Frances Kirwan, Jonathan Woolf An Introduction to Intersection Homology Theory, ISBN 1584881844
- Kleiman, Steven. The development of intersection homology theory. A century of mathematics in America, Part II, Hist. Math. 2, Amer. Math. Soc., 1989, pp. 543–585.
- Hazewinkel, Michiel, ed. (2001), "Intersection homology", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1556080104, http://www.encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=I/i052000